The Ostara Newsletter: First Anniversary edition
Authors: Priyamvad Ranade & Vasudha Madhavan
Hello everyone, here we are with our First Anniversary edition of the Ostara Newsletter! Yes, we started publishing “All Above EVs” exactly a year ago. As the first and only electric mobility-focused investment bank in India, we love to learn and share insights & key developments and showcase interesting startups in the Indian EV ecosystem. We feel truly grateful for the love this newsletter has received over the past year and look forward to continuing this journey into the next year and beyond!
In this edition, we continue with Part 2 of our 4-part series on the Indian Charging landscape and we also have a long-overdue Ostara update at the end of this edition! Hope you enjoy the read and don’t forget to share your thoughts and feedback, as always.
Previously, on the Ostara Guide, we talked about protocols and guidelines for Safe Charging Stations, along with an introduction to the key stakeholders in the Charging landscape. This month we shine the spotlight on the Charge-point Operator or the CPO.
Who is a CPO?
While CPOs (Charge-point Operators) install and operate charging stations, they also offer diagnostics, maintenance, tariff management, and other value-added services to provide smooth network operations. CPOs may also own the charging infrastructure or simply provide the platform solutions to owners of EV charge points.
The Key Value Proposition of a CPO:
Access to residential, public or destination charging services for EV users
Software-enabled Charge-point Management and maintenance services, enabled by software
Access to charging network & usage data for B2B partners
CPO is a key customer for the EV Supply Equipment (EVSE) OEM
The Revenue Streams of a CPO typically comprise of:
One-time or recurring fees from charging station installation, management and maintenance
Usage fees for Charging paid by EV users
Subscription fees from deployment of own Charge-point Management software
The Cost Structure of a CPO typically comprises of:
Cost of supplied energy, including initial connection costs
Purchase cost of chargers and related EVSE
Lease or ownership costs for the charging station location
Management and maintenance costs
Software development costs
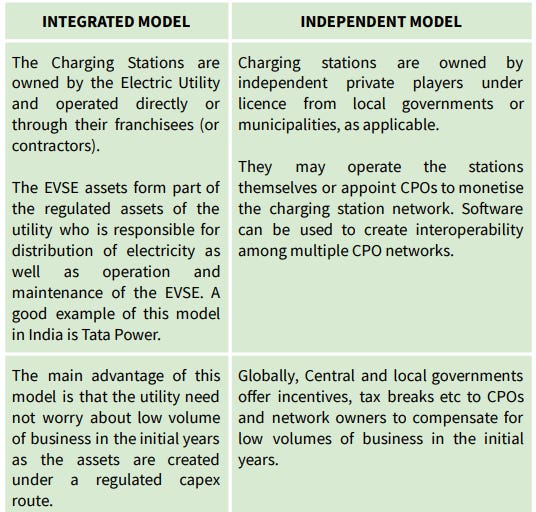
CPO Business Models
Source: ISGF
Use-cases for EV Charging
EV charging infrastructure specs vary depending on use-case, customer needs, and the parties involved. While home charging may take place on an AC slow charger, in public charging, a vehicle owner may pay a premium to have the battery recharged faster in using DC Fast chargers.
Source: McKinsey
Leading CPOs in India
Key Success Factors for a CPO
Dense network of charging stations: EV charging solutions space is quickly getting competitive with many startups. In order to create a dense footprint, it is very important to have a highly replicable model to increase the number of installations.
Target Market: Very important to clearly identify a target customer-base, which should be accessible and large enough, to create a scaled business.
Effective real-estate partnerships: Location and real-estate play a crucial role in branding and footprint for the CPO. Revenue-sharing partnerships with location-owners can help make the CPOs business model asset-light.
Good Power grid connectivity: The electricity supplied to the charge-stations comes from the power grid, and good connectivity between the two is very important for efficient and uninterrupted function of the charge-stations.
Charging Software: Software will become the key strength and the basic necessity for Charging operators going forward, helping leverage and monetise own and third-party charger networks, as well as integrating with OEMs & Fleets for connected EVs.
Role of Government Subsidies: Governments offer financial subsidies, concessional land provision and/or energy supply to incentivize CPOs to reduce capital costs of implementation
Recent Deals & Developments
May 2022: Tata Power signed an MoU with the National Real Estate Development Council (NAREDCO), Maharashtra, to install up to 5,000 electric vehicle (EV) charging points across its member’s developer properties.
May 2022: Magenta Chargegrid joins hands with BSES Rajdhani Power Limited, Delhi’s state electricity supplier, to install private home EV chargers in Delhi.
May 2022: goEgoNetwork partners with facilities management major Handiman Services Limited. Through this partnership, goEgoNetwork will be providing exclusive EV charging solutions to the commercial and residential complexes managed by Handiman Services Limited.
May 2022: BYD India, the Indian subsidiary of Warren Buffett-backed EV manufacturer - BYD, has partnered with three electric vehicle charging network providers ChargeZone, Volttic, and Indipro to access 950+ charging stations across India.
May 2022: India’s first Biogas-powered EV charger makes its debut in Mumbai. In partnership with the Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai, AeroCare Clean Energy installed the Biogas-powered EV charger. The system has been given a grant from the Department of Biotechnology (BIRAC) as well as the Government of India.
Ostara Update!
I’m happy to share that Mukund Ranganathan is partnering with me in scaling up the Mobility and Energy practice at Ostara Advisors. Mukund is a seasoned investment banker with 26 years of experience in advising corporates on M&A and capital raising transactions across deals in automotive and industrials, including advising India’s first EV company, Reva Electric on private equity raising way back in 2007!
He served most recently as Co-Head of Motilal Oswal Investment Banking, prior to which he led the Advisory and M&A practice at Edelweiss and had a 9-year stint at Morgan Stanley in Mumbai. Mukund and I are working together to consolidate Ostara's leadership position in Electric Mobility.
Founder & CEO
About Ostara Advisors